WHAT IS GOUT?
When you are in the middle of a painful gout attack, you may feel like you are the only one dealing with gout. But you are not alone. According to the National Arthritis Data Workgroup, an estimated 6 million people in the U.S. report having experienced gout at some point in their lives. In fact, gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40.
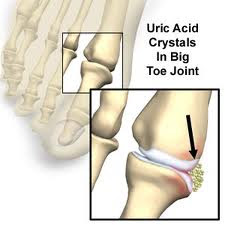
So, what exactly is gout? We know that it's a form of arthritis that is caused by high uric acid levels in your blood(hyperuricemia). Gout attacks occur when excess uric acid forms crystals, causing inflammation in your joints that leads to swelling and pain. As your uric acid level rises, so does the potential for gout and gout flares. Over time, gout attacks can become more severe, last longer, and occur more often.
Decreasing your uric acid to the recommened level(less than 6 mg/dL) can reduce the risk of gout attacks over the long term.
GOUT SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
Gout flares usually strike suddenly, at night, and without any warning. During the attack, the affected area becomes hot, red, swollen, and extremely tender. Having gout may sometimes feel like your toe is a volcano erupting into a hot, fiery flare. Gout may be best known for causing severe pain in the toe. In fact, most gout attacks occur in the big toe. However, you may be surprised to learn that gout attacks can occur in other parts of the body as well.
Who gets gout? There are certain characteristics that affect your likelihood of experiencing gout:
- Men, especially between the ages of 40 and 50, are more likely to develop gout than women.
- Most women experience gout after menopause.
- There may be a genetic link: many people with gout have a family history of the disease.
- Gout rarely affects children or young adults.
- People with certain conditions are at a higher risk for gout. These conditions include diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and/or kidney problems.
Gout symptoms may look a bit different in people over 60 years of age. For one thing, the joints in the upper part of their body are more likely to be affected than the joints in the lower body. And, people over 60 often experience painful gout attacks in mor than one joint at the same time.
source: http://www.gout.com/
No comments:
Post a Comment